ESG Disclosure
Sound ESG management requires not only establishing an ESG framework but also ensuring robust ESG disclosure.
Investors make decisions based on external assessments of companies’ ESG performance, and such investment behavior contributes to a virtuous cycle in which strong ESG practices ultimately lead to improved financial performance.
Investors make decisions based on external assessments of companies’ ESG performance, and such investment behavior contributes to a virtuous cycle in which strong ESG practices ultimately lead to improved financial performance.
- Key Global Trends in Sustainability Reporting
-
Leading global companies have steadily increased the rate at which they publish sustainability reports.According to KPMG’s 2024 survey on global Sustainability Reporting trends, 79% of N100 companies (a total of 5,800 firms) and 96% of G250 companies (a total of 250 firms) publish sustainability reports.
N100 comprises the top 100 companies by revenue in 58 countries, selected by KPMG experts. G250 refers to the top 250 companies by revenue among the Fortune Global 500 companies in 2023.
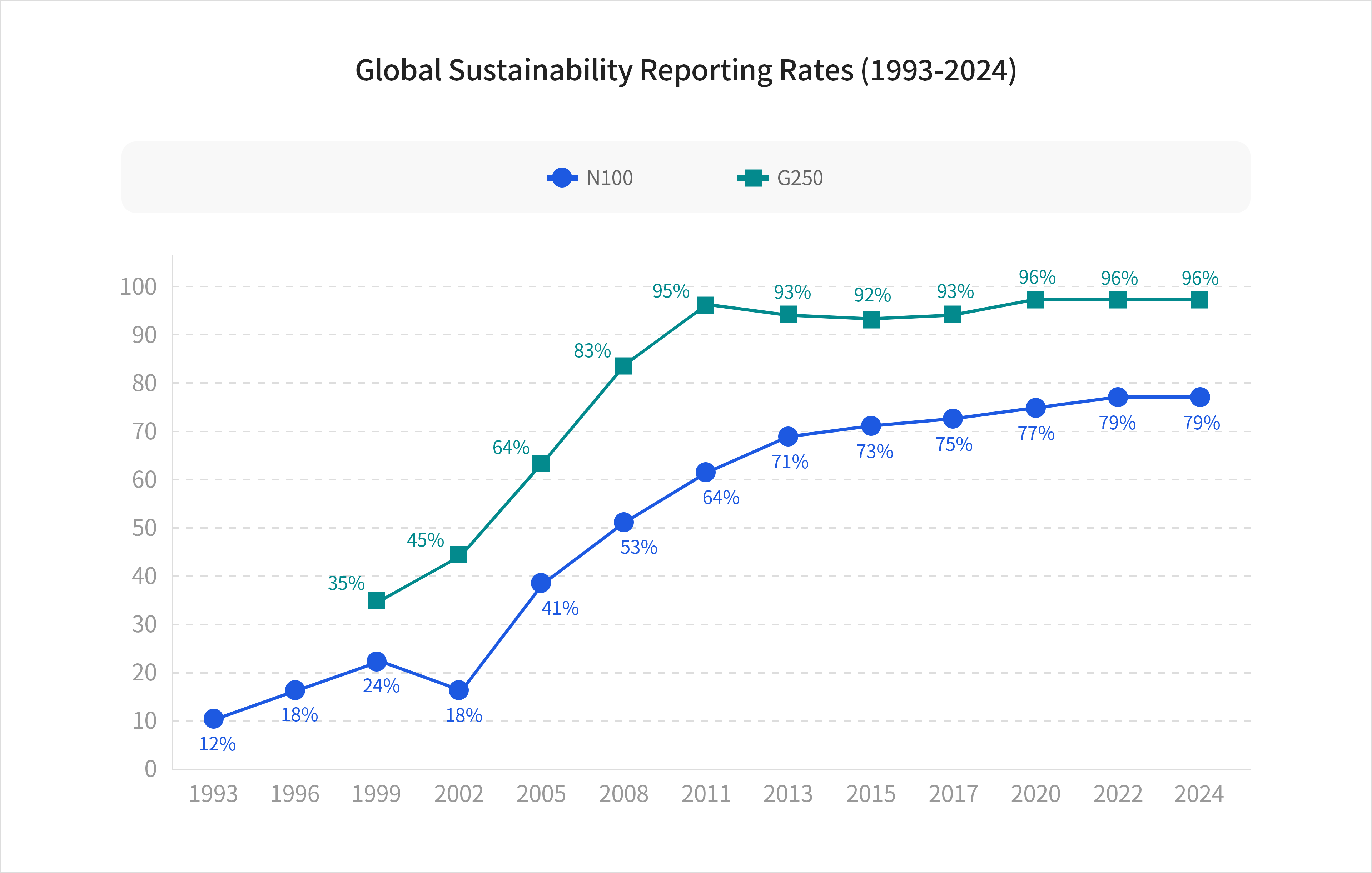

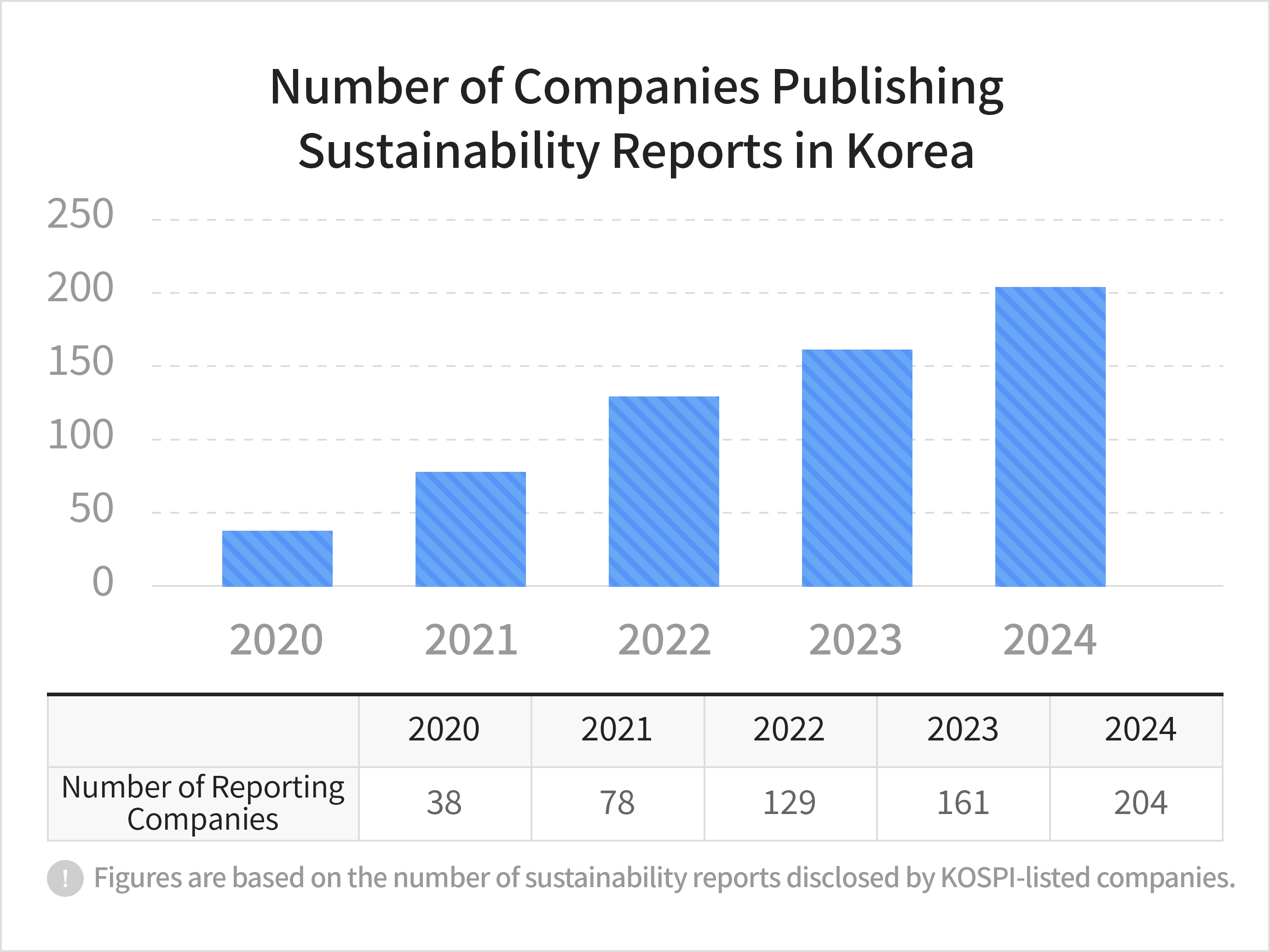
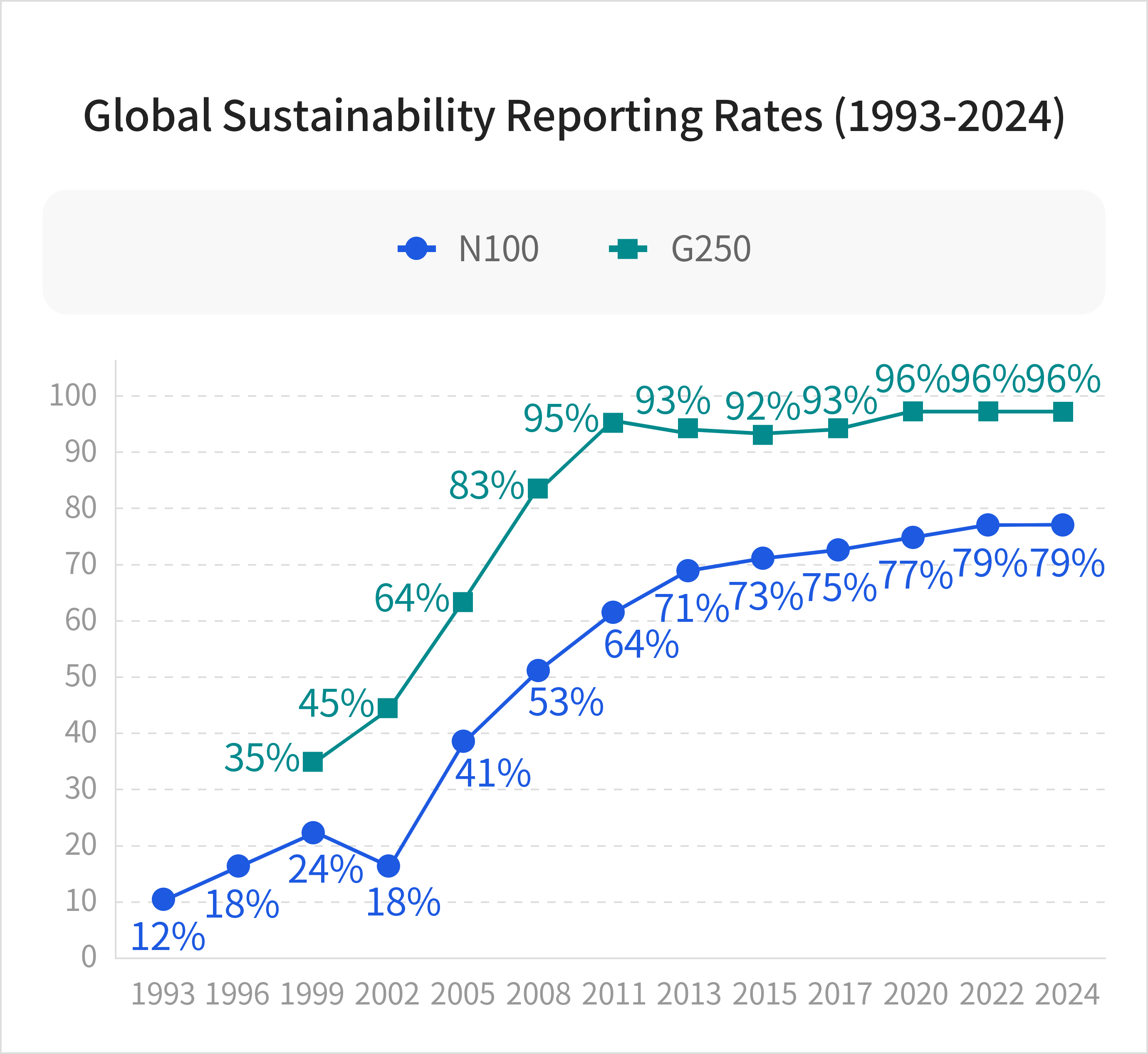 Source: KPMGDomestic companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of ESG disclosure and are publishing separate ESG reports to strengthen their ESG management practices.Over the past five years, the number of KOSPI-listed companies voluntarily issuing sustainability reports has continued to grow. Although sustainability reporting is not mandatory, an increasing number of companies voluntarily disclose ESG-related information each year to provide investors with insight into their ESG practices.
Source: KPMGDomestic companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of ESG disclosure and are publishing separate ESG reports to strengthen their ESG management practices.Over the past five years, the number of KOSPI-listed companies voluntarily issuing sustainability reports has continued to grow. Although sustainability reporting is not mandatory, an increasing number of companies voluntarily disclose ESG-related information each year to provide investors with insight into their ESG practices.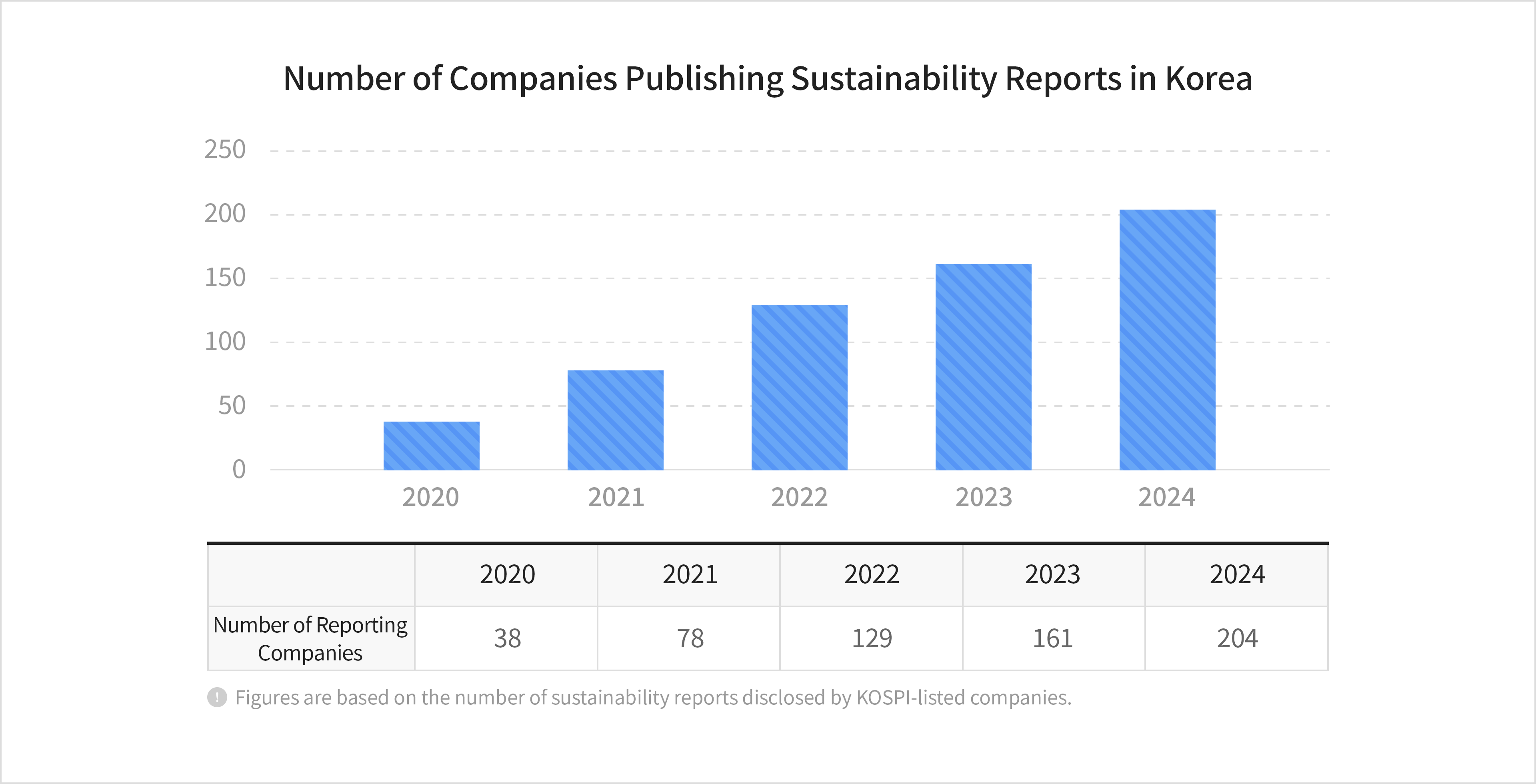

- ESG Reporting Standards
-
Companies in Korea and around the world prepare ESG reports using various global disclosure standards, including GRI, SASB, and TCFD. In addition, jurisdictions such as Korea, the European Union, the United States, Japan, and Australia are actively developing their own sustainability disclosure frameworks.


 Source: Center for Social value Enhancement Studies(CSES)
Source: Center for Social value Enhancement Studies(CSES) - Key Global Standards in ESG Reporting
-
Standards Key Characteristics IFRS S1, S2 - Sustainability disclosure standards issued by the ISSB (International Sustainability Standards Board) under the IFRS Foundation.
- IFRS S1 sets out general requirements for sustainability-related disclosures useful to investors, while IFRS S2 provides specific requirements for climate-related disclosures.GRI Standards - The world’s first sustainability reporting standards.
- Comprised of Universal Standards, Sector Standards, and Topic Standards.TCFD Recommendations - A framework for climate-related financial disclosures.
- Structured around four thematic areas: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics & Targets.SASB Standards - Industry-specific standards focused on sustainability issues most likely to have a material financial impact.
- Cover 77 industries across 11 sectors, each with tailored ESG disclosure metrics.