ESG History
- How ESG Emerged
-
ESG may feel like a newly emerging buzzword, but it is not unfamiliar. The concept originates from sustainable development—meeting today’s needs while protecting the future for the next generation. Building on this idea, ESG frames corporate sustainability and long-term growth around three core values: environment, society, and governance.Sustainable Management


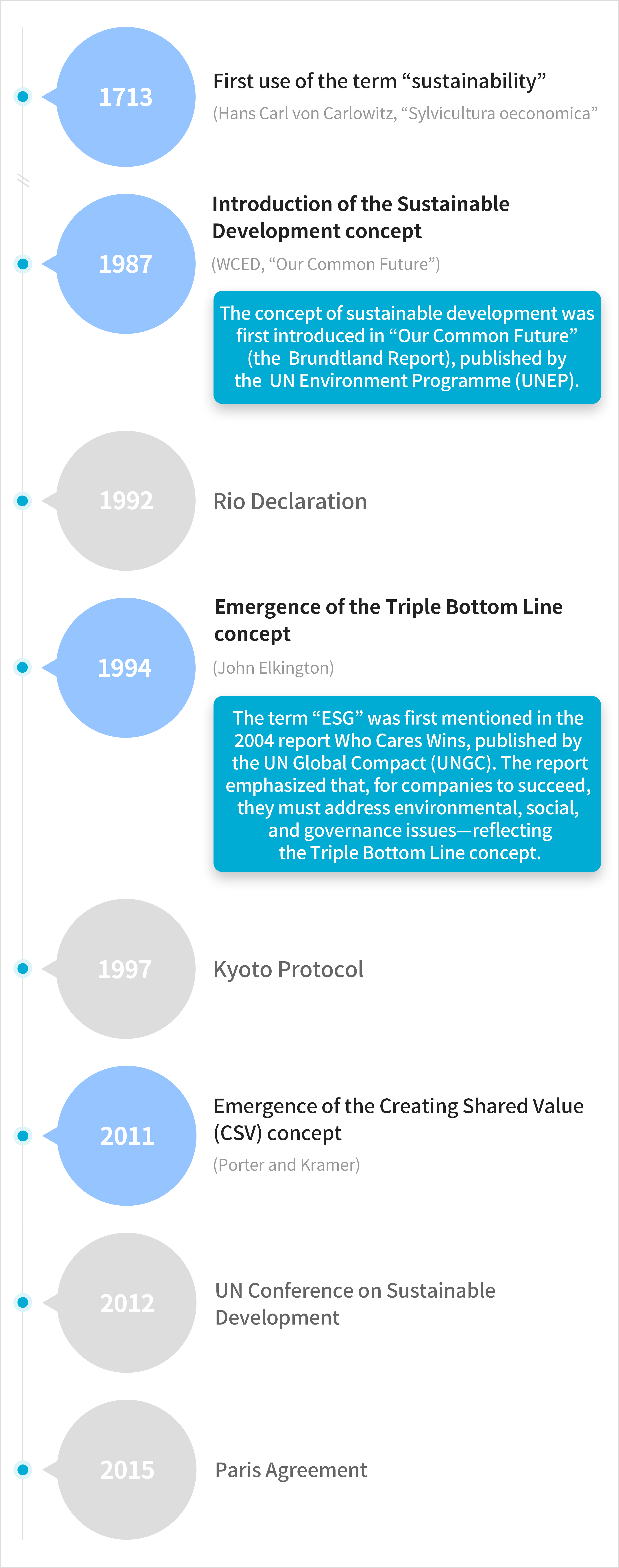
Sustainability Improving the quality of human life while living within the carrying capacity of supporting eco-systems (1991, UNEP, Caring for the Earth : A strategy for Sustainable Living)Sustainable Development Meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs (1987, WCED, Our Common Future)Sustainable Management A business paradigm that pursues sustainable development based on an organization’s economic, social, and environmental responsibilitiesSustainable management represents a more fundamental concept than ESG. Today, ESG can be understood as the evolution and institutionalization of sustainable management and corporate social responsibility (CSR). As expectations for the relationship between business and society have shifted over time, a deeper understanding of sustainable management helps make ESG more widely applicable. The term “sustainability” was first introduced in 1713, and the most widely accepted concept was established in the 1987 report Our Common Future. Later, the introduction of CSR and the concept of Creating Shared Value (CSV) shaped ESG into a new paradigm.A Brief History of Sustainable Management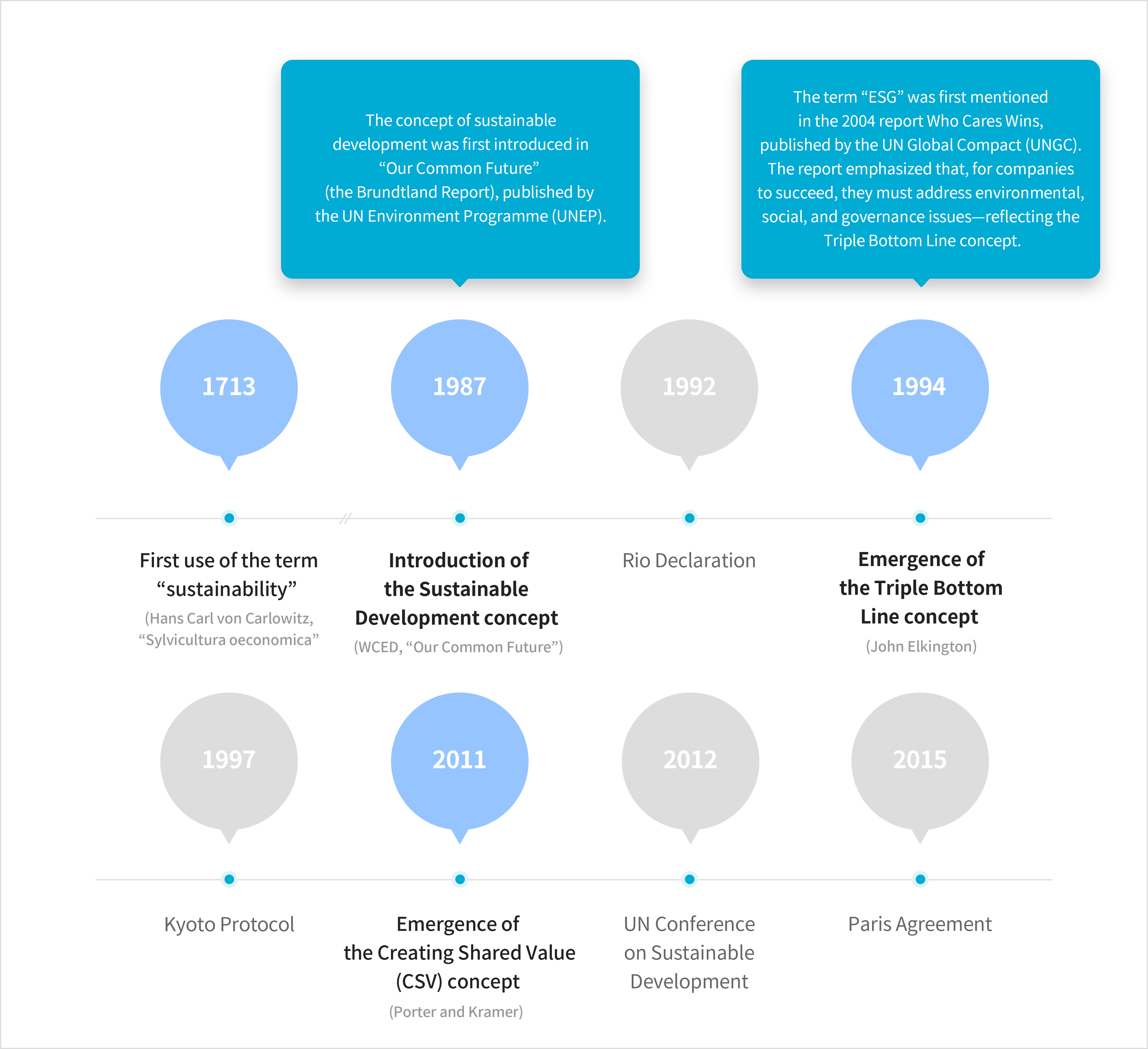

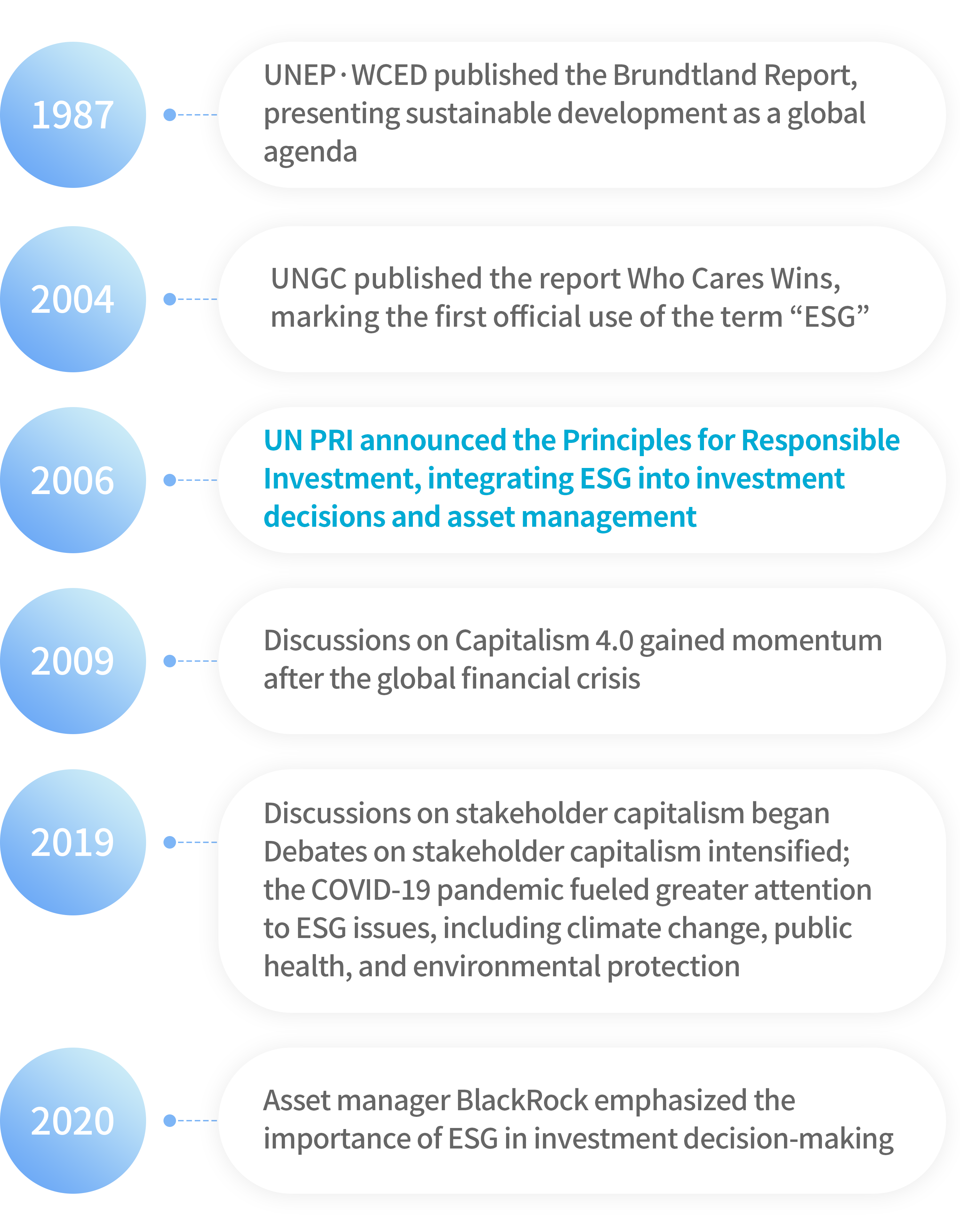
 The term “ESG” was first officially used in the 2004 report Who Cares Wins, published by the UN Global Compact (UNGC). Subsequently, in 2006, the Principles for Responsible Investment (UN PRI), an alliance of international investors, emphasized ESG as an investment principle, laying the foundation for the ESG framework that is central to today’s corporate management. With the emergence of Capitalism 4.0 and stakeholder capitalism discourses, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated global attention to ESG issues such as climate change, public health, and environmental protection. In line with this trend, ESG investing—actively incorporating ESG information into long-term investment decisions—has entered the mainstream.
The term “ESG” was first officially used in the 2004 report Who Cares Wins, published by the UN Global Compact (UNGC). Subsequently, in 2006, the Principles for Responsible Investment (UN PRI), an alliance of international investors, emphasized ESG as an investment principle, laying the foundation for the ESG framework that is central to today’s corporate management. With the emergence of Capitalism 4.0 and stakeholder capitalism discourses, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated global attention to ESG issues such as climate change, public health, and environmental protection. In line with this trend, ESG investing—actively incorporating ESG information into long-term investment decisions—has entered the mainstream.