Understanding ESG
- What is ESG?
-
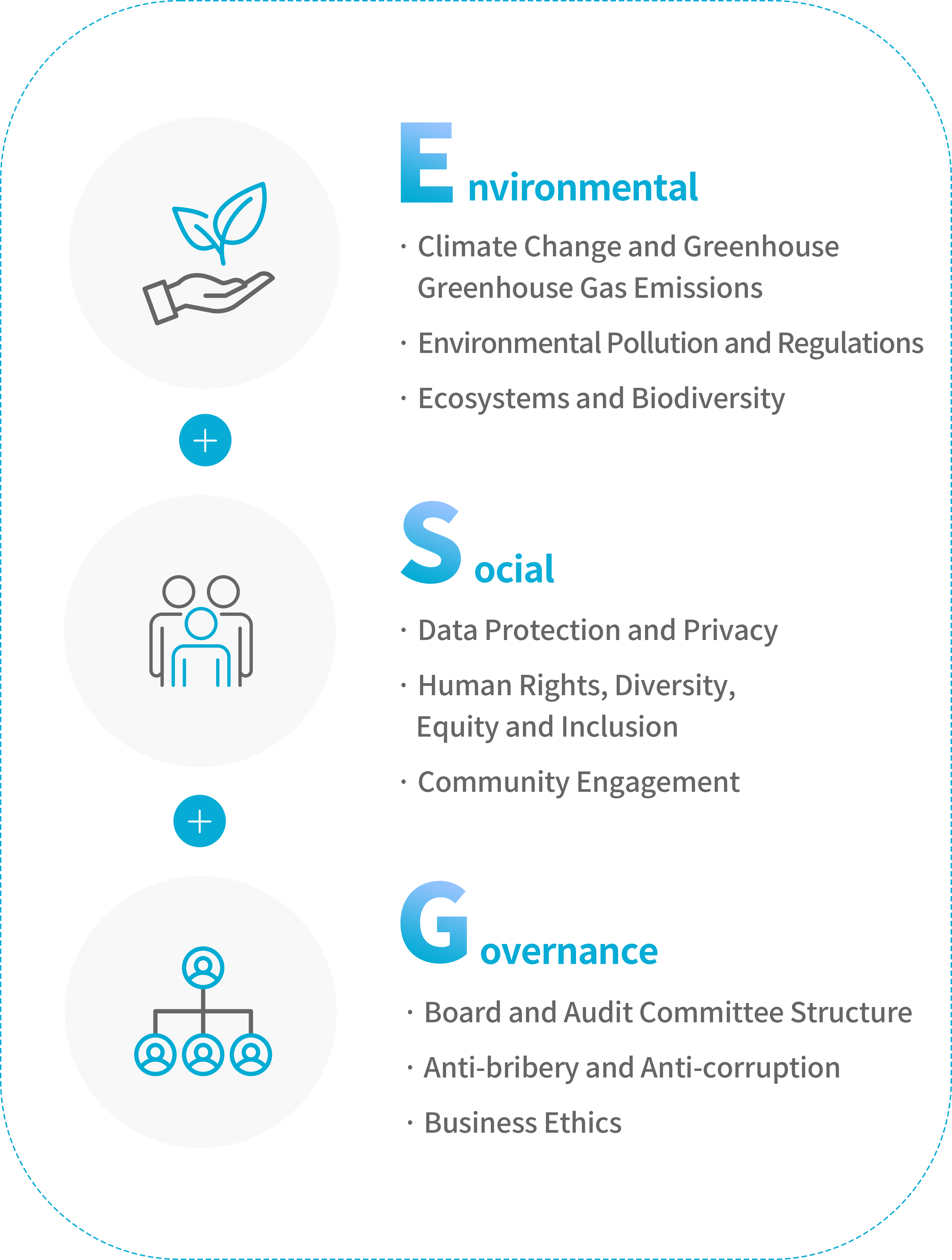
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance — three core pillars of corporate sustainability.
These factors are directly tied to a company’s long-term growth and sustainability. Below are the key components of ESG.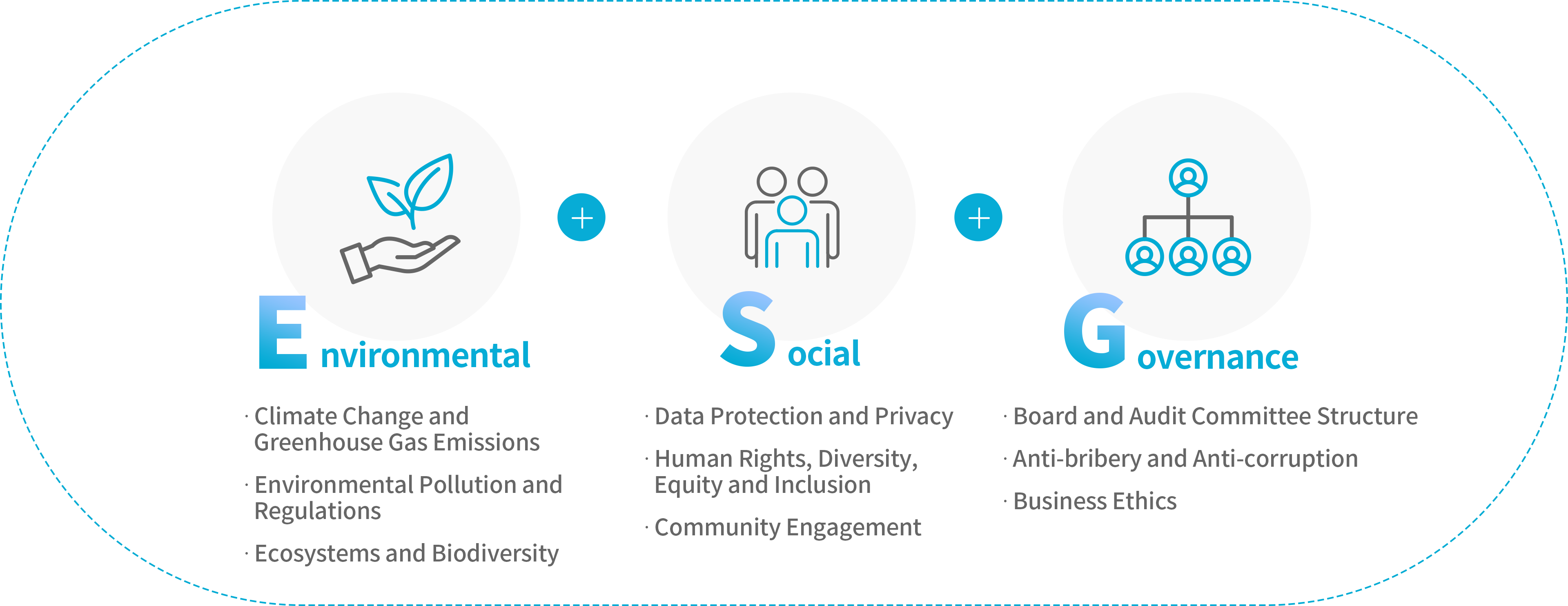

 In the past, corporate evaluation primarily focused on financial metrics — how much was invested and how much was earned. Today, however, the growing impact of issues such as climate change has highlighted the importance of non-financial metrics in assessing a company’s true value. As awareness of corporate social responsibility expands, both investors and consumers increasingly emphasize non-financial value alongside financial performance.
In the past, corporate evaluation primarily focused on financial metrics — how much was invested and how much was earned. Today, however, the growing impact of issues such as climate change has highlighted the importance of non-financial metrics in assessing a company’s true value. As awareness of corporate social responsibility expands, both investors and consumers increasingly emphasize non-financial value alongside financial performance.


- ESG Definition
-
ESG is defined differently depending on the institution’s mission, business type, and stakeholders. Commonly presented keywords include investment decisions, long-term returns, financial value, corporate risks, social responsibility, and sustainability. In capital markets, ESG encompasses the critical non-financial factors that influence long-term financial value and guide investment decisions.
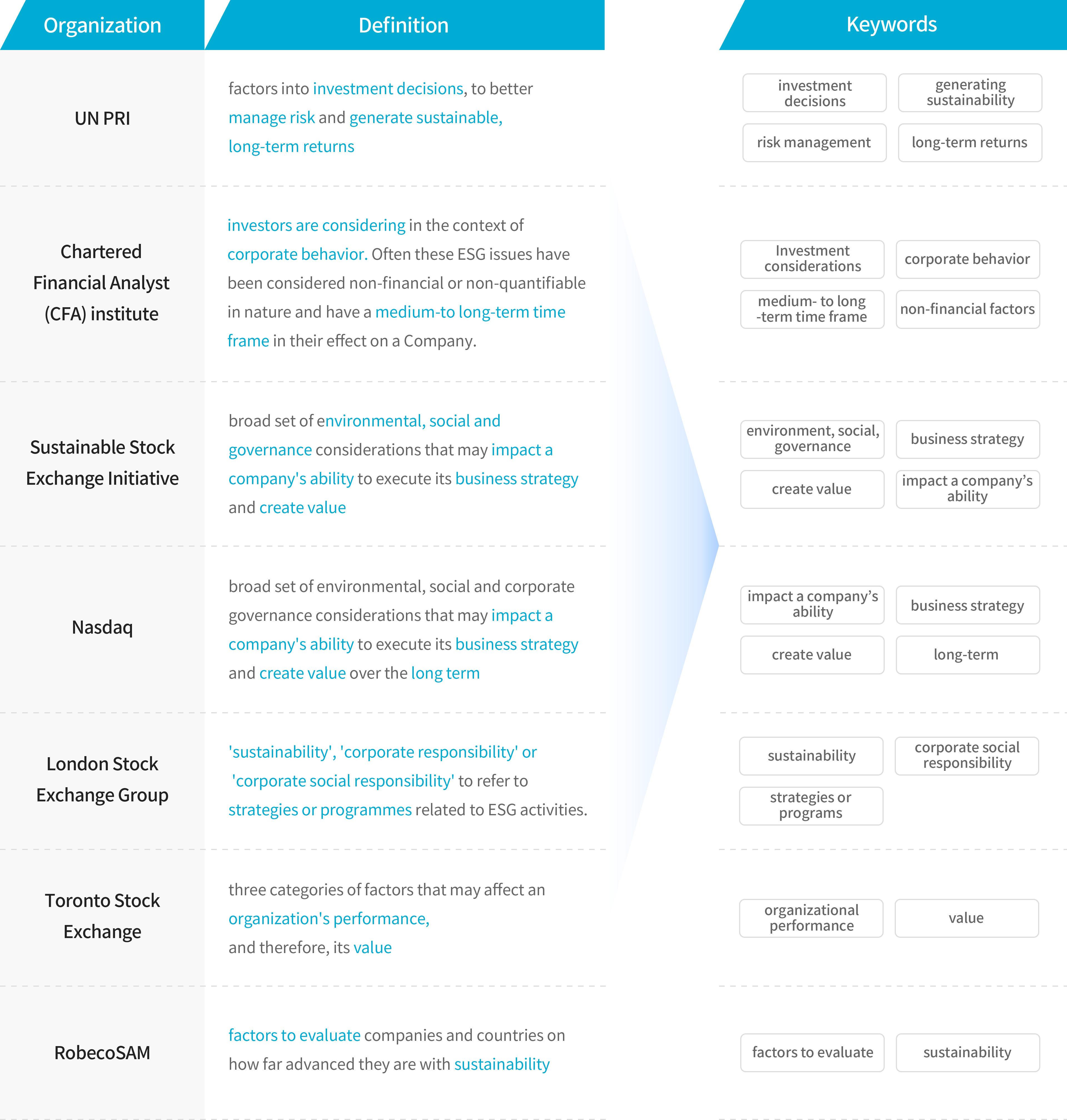

 ESG can be interpreted from normative, integrated, instrumental, and political perspectives.
ESG can be interpreted from normative, integrated, instrumental, and political perspectives.